A plasma drug concentration-time profile is usually the net effect of two simultaneous processes: (1) absorption of the drug from the GI tract. As absorption is proportional to drug dissolution thus absorption and dissolution are used interchangeably; (2) elimination of the drug from the blood. These two actions, and their net effect, are represented by three profiles and are shown in the figure.
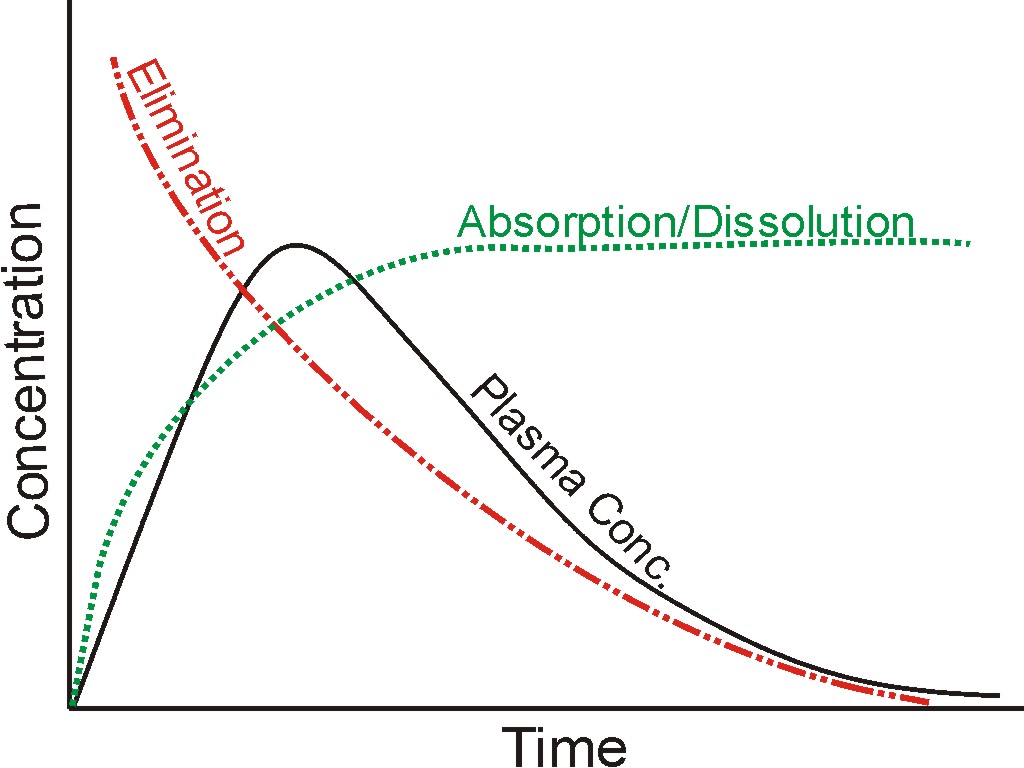
In mathematical terminology, these three curves (profiles) are functions: dissolution or absorption as input, blood concentrations as output, and elimination as the weighting factor or function. To further simplify, in the analogy of linear regression used for calibration curves, output function may be considered as “Y or dependent variable,” “X or input function,” and “M or slope/proportionality constant.” In linear regression analysis, X, Y, and M parameters have values (numbers); however, these are functions in the case of drug concentration profiles. So solving these function-based equations is a bit more complicated.
The procedure is similar to that of linear regression, commonly used to establish calibration curves and then use the calibration curve to determine the unknown concentrations or response (e.g., absorption or peak height/area values). So, if “Y” is known, then “X” may be determined and vice versa. Similarly, if the input function is known, one can determine the output function and vice versa. Determining output function (plasma blood concentrations), if input function (dissolution results) is available, the procedure will be called convolution technique. The inverse of it that is obtaining input function (absorption/dissolution results) if output function is provided, the procedure will be called deconvolution.
There are computer software available that provides the capability of solving for a function when the others are available. However, the convolution approach could be simpler where commonly available spreadsheet software may also be used. For further detail see, Qureshi, SA. In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation (IVIVC) and Determining Drug Concentrations in Blood from Dissolution Testing – A Simple and Practical Approach. The Open Drug Delivery Journal, 2010, 4, 38-47. (Link)
